An abscessed tooth is a dental condition in which the nerve, also referred to as the dental pulp, has become infected.
The infection usually occurs when a dental cavity (tooth decay) goes untreated and spreads deep within the tooth. The infection can also occur from a broken or cracked tooth where the dental pulp is exposed to the oral environment. The bacteria that cause an abscess can spread down the length of the roots and into the surrounding bone tissue. Some dental professionals also consider an infection between the gum and tooth root a tooth abscess. Additionally, the dental nerve can be susceptible to necrosis (infection) after a crown or large filling are completed. The closer the dental treatment approaches the dental nerve the more likely the nerve can become affected. The dental nerve can be variable in size and infection after dental treatment is usually not the fault of the dentist. Teeth that are directly subjected to dental trauma (for example, from a fall or from a hit by a projectile such as a baseball) should be immediately examined by a dental professional.
What are the symptoms of an abscessed tooth?
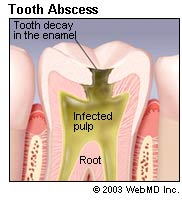 Common symptoms of a dental abscess include swelling, pain when chewing, a constant toothache or a dull, constant throb associated with the tooth. Other symptoms may include swelling of the glands of the neck, fever, bad breath, and odd or bitter taste in the mouth. Drainage from the gum tissue may also be present. The gum tissue can become inflamed, swollen, or infected. A small pimple on the gingival tissue referred to as a sinus tract may also develop and is usually representative of a dental infection. The abscess can be painful but occasionally the problem can go unnoticed unless detected by a dental professional.
Common symptoms of a dental abscess include swelling, pain when chewing, a constant toothache or a dull, constant throb associated with the tooth. Other symptoms may include swelling of the glands of the neck, fever, bad breath, and odd or bitter taste in the mouth. Drainage from the gum tissue may also be present. The gum tissue can become inflamed, swollen, or infected. A small pimple on the gingival tissue referred to as a sinus tract may also develop and is usually representative of a dental infection. The abscess can be painful but occasionally the problem can go unnoticed unless detected by a dental professional.
To read more, and to see Dr. Sherman’s original web publication, click HERE.
Thanks for visiting Tri City Micro Endodontics.
